Medicinal Cannabis Information
The Cannabis Plant has been long revered throughout history for it’s myriad of uses, including its powerful and sustainable medicinal properties.
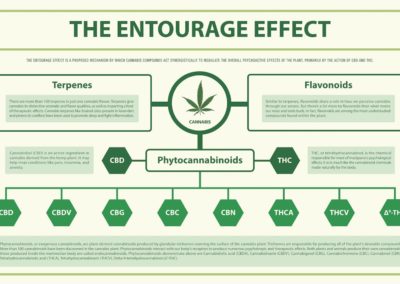
Cannabis itself contains hundreds of healing compounds, most commonly cannabinoids and terpenes.
Evidence-based endocannabinoid medicine combines different ratios of cannabinoids and terpenes to treat a variety of symptoms associated with common medical conditions such as: anxiety, depression, sleep disorders and pain.
Medical cannabis is thoughtfully cultivated, carefully harvested and meticulously crafted into clean, safe, oils, tinctures and flowers for patient use.
Medical Conditions Which May Qualify for Cannabinoid Medicine:
- Cancer Pain
- Palliative Care
- Epilepsy
- Nausea and Vomiting related to Chemotherapy
- Fibromyalgia
- Spasticity from Neurological Conditions
- Anorexia and Wasting
- Associated with Chronic Illness
- ADHD
- Autism
- Chronic Pain
- Anxiety
- Chronic Insomnia
- Migraine
- Neuropathic Pain
- Multiple Sclerosis
- PTSD
- IBS
- Movement Disorders
Medicinal Cannabis may be consumed orally through the use of oils and tinctures or through vaporising flower in a small, handheld device.
Oral consumption results in a slower onset but more sustained effect, while vaporizing flowers will take rapid effect with shorter lasting results, but with peak physiological and psychological effects.
As each patient is different, your doctor will tailor the frequency, dose and method of your medicine specifically for your needs using a combination of cannabinoids and terpenes specific to treating your condition.
There are over 100+ known cannabinoids that are used to manage the symptoms of varying conditions. When you discuss cannabis medicine with your doctor, it’s important to know that there are three main compounds you will commonly discuss:
THC
One of the major cannabinoids which has therapeutic potential as an analgesic, anti – inflammatory and anti – nausea / anti – vomiting agent. THC possesses psychoactive properties and is responsible for the “high” feeling experienced by some patients. In very low doses, THC can help to manage feelings of anxiety, and may have a positive impact on sleep without having an intoxicating effect on the patient.
CBD
A non – intoxicating cannabinoid gaining favour with prescribers for its strong medicinal properties. Research on CBD shows that it may reduce pain, anxiety and inflammation. It has also been found to be a potent anti – epileptic agent. Patients using THC for it’s benefits should know that CBD will counter it’s psychotropic effects, making it a non-psychotropic compound.
Terpenes
The terpene profile of a product not only determines the scent and flavour but may also influence how each variety of cannabis impacts each person. Terpenes are suspected to have medicinal properties of their own, in addition to working with CBD, THC, and other cannabinoids to produce the overall therapeutic effect of a product.
There are over 100 known cannabinoids. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are the most commonly discussed. The cannabis plants contains over 400 different compounds including over 300 non – cannabinoids.
Anandamide is the most studied endocannabinoid in the human body and was discovered in 1993. The name is derived from the sanskrit word “ananda” meaning bliss or delight, which is one of the main cerebral effects of anandamide. Anandamide receptors are the primary molecular target responsible for the pharmacological effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the psychoactive ingredient in cannabis.
Dr Mehdi Samari and Dr Lucy Wang are authorised prescribers of medicinal cannabis at Milsons Point Medical Centre.
Disclaimer: Most Medicinal Cannabis are not registered in Australia by TGA (not listed on Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods). All patients should consult their healthcare professionals for further advice.